
Sustainable Hydropower
Status
Ongoing
Overall Project Duration
2023–2026
Commissioner
N/A
Political Partner
State Electricity Company (PLN)
Cooperation Partners
State Electricity Company (PLN)
Implementing Organization
KFW
Project page on organization website
- N/A
Project Documents and Links
- N/A
The aim of the project is to improve the supply of electricity to the Indonesian population through sustainable hydropower in an inclusive, climate and environmentally friendly manner. The project contributes to environmental and climate-damaging emissions by: Sustainable, reliable and comprehensive supply of electricity to the country contributes to the environmentally sustainable development of Indonesia.
Background
The FC module ‘Sustainable Hydropower’ supports the state electricity supplier and project promoter Perusahaan Listrik Negara (PLN) in expanding renewable energy to meet the growing domestic demand for electricity. The project implements investment measures for the construction, expansion or rehabilitation of hydropower plants. Currently, KfW supports three hydropower projects located in North Sumatra (Kumbih), North Sulawesi (Sawanga) and South Sulawesi (Bakaru) which aim to increase the production of clean energy through hydropower and hereby at enhancing energy infrastructure and contributing to Indonesia’s energy security and environmental goals.
Project Approach
N/A
State of Implementation
For the Kumbih hydropower project, the loan agreement was signed in December 2017. Since then, the detailed design of the power plant and the construction of the base camp have been completed, setting the stage for the start of construction of the Kumbih hydropower plant, which is expected to be completed by the end of 2027.
The loan agreement for the Bakaru hydropower project was signed with a government guarantee to PLN in 2019. Since then, PLN has signed the contract with the project implementation consultant in 2020 and the feasibility study for the project has been updated. We currently expect the construction of the Bakaru HPP to be completed by the end of 2027.
For the WKW Sawangan site, preliminary work is currently underway and the completion of the feasibility study and the environmental and social study in 2021 will mark a significant milestone in the project development, with the HPP Sawangan planned to be completed by the end of 2030.
Project Activity Areas (Outputs)
Informed social dialogue and stakeholder engagement on just energy transition in coal regions takes place in Regional Consultation Forums
Transformational measures to support the JET of coal regions are rolled out
Policy advice to improve the policy framework for just energy transition is fed into respective policy processes.
Project Publications
Tools
SEA Information Platform for the Energy Transition (SIPET)
The Southeast Asia Information Platform for Energy Transition (SIPET) is a one-stop platform for information and knowledge exchange about the energy transition in the region. SIPET aims to be a central launch pad for energy transition stake holders to facilitate dialogue and promote coordination in the Southeast Asia power sector.
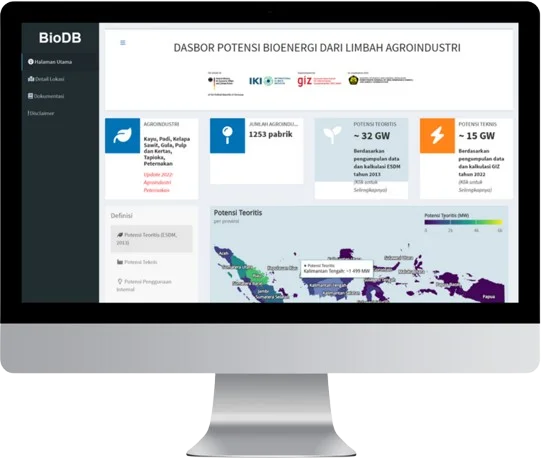
Bio DB
BioDB is a useful website for providing general information, encouraging discussion and conversation on the topic of bioenergy from agro-industrial waste. The data and information presented were collected by the Strategic Exploration of Economic Mitigation Potentials through Renewables (ExploRE) project, a project funded by the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU), Federal Republic of Germany, in collaboration with the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM) of the Republic of Indonesia, and implemented by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
IKI JET
The global energy transition away from coal to renewable energy is threatening local livelihoods, economic activities and jobs, but also holding opportunities for sustainable, low carbon development. The project aims at supporting key stakeholder of coal regions to plan for and implement regional just energy transition pathways away from coal and towards a low-carbon energy system. Focusing on the regional economic transformations, the project works with government, industry, unions, communities, civil society, and academia. It supports interregional peer-to-peer exchange, learning, and policy dialogue in an international network and information sharing via a knowledge hub. In Indonesia, it supports the development of specific transition plans in two coal regions. In Colombia, it supports the development of the concept and framework for energy communities and the implementation of just and inclusive energy communities in César and la Guajira.

CASE for Southeast Asia
The “CASE for Southeast Asia” website is dedicated to the promotion of clean, affordable, and secure energy transitions across Southeast Asia. The website focuses on the provision of resources, the conducting of research, and the facilitation of collaborative projects in countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, the Philippines, and Vietnam, with the aim of supporting energy transition efforts. The platform highlights the challenges and opportunities in the region’s energy sector, while sharing knowledge, best practices, and policy recommendations aimed at advancing the transition to renewable energy and sustainable development

Contact
Project Address
TBD
- N/A
- N/A
Andre
Taken from Master_Energy Cooperation Mapping
















